
Living With BPH
BPH Statistics1,2
of men ages 51-60 have BPH
of men say BPH impacts how they feel about themselves
of men say BPH impacts their quality of life
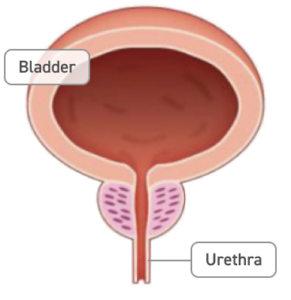
Normal Prostate
Urine flows normally from the bladder, through the prostate, and out of the body.
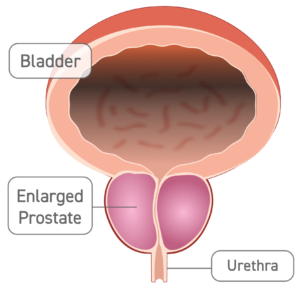
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
An enlarged prostate makes it difficult to urinate normally.
Prostate Enlarged
Prostate
WHAT IS BPH?
The prostate is a gland that plays an important role in sexual function. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate, is a prostate that has grown to be larger than normal. BPH is not prostate cancer.
As the prostate grows, it may:
- Constrict the urethra, making it difficult to urinate
- Apply pressure on the bladder, causing it to weaken and have difficulty emptying
Left untreated, BPH can cause significant health problems, including irreversible bladder or kidney damage, bladder stones, and incontinence.
WHAT CAUSES BPH?
The cause of prostate enlargement is not known.
What is known is that there are two phases of growth:
- During puberty, the prostate doubles to about the size of a walnut and then stops growing
- Around age 25, the prostate continues to grow for the rest of a man’s life
HOW COMMON IS BPH?
BPH is an unfortunate reality of aging for many.
Today, the condition is estimated to affect3:
94 Million Men Actively Managing BPH Globally
are in their 50s
are in their 60s
are in their 70s
Have BPH1
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF BPH4
BPH may cause symptoms called lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). LUTS affects the bladder, prostate, and urethra and can impact your ability to hold urine and empty the bladder.
Experiencing BPH Symptoms? You’re Not Alone.
of men over 50 years of age will encounter moderate to severe LUTS
of men will experience moderate to severe LUTS by the time they are 85 years of age, which is likely caused by BPH
CATEGORIES OF BPH SYMPTOMS

Ability to Hold Urine
BPH can impact your ability to hold urine in various way. No matter the symptoms, they all can be challenging to deal with.
Common indicators in this category include:
Urgency
The need to urinate immediately or urgently
Frequency
The need to urinate more often than normal
Nocturia
The need to urinate frequently at night while sleeping
Intermittency
A urine stream that starts and stops

Emptying the Bladder
Men with BPH can have trouble emptying the bladder and may experience various forms of discomfort while trying to use the toilet.
Common indicators in this category include:
Straining
The need to push or strain to start and complete urinating
Weak Stream
Gentle or weak stream instead of a strong stream of urine
Dysuria
Pain or stinging when urinating
Hesitancy
Difficulty starting to urinate
Incontinence
Complete loss of the ability to hold urine
Retention
Complete loss of the ability to empty your bladder

The Impact of BPH on Quality of Life
Regardless of the symptoms, BPH presents several inconveniences to everyday life that no one should have to face.
Common indicators in this category include:
Inability to sleep through the night
Limits on social activities due to toilet proximity
Embarrassment and frustration
Relationship challenges
Difficulty in professional life
Decreased sexual function (erectile function/ejaculatory function)
Are you experiencing BPH symptoms?
Take the International Prostate Symptom Score assessment and see how severe your symptoms are.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT

Diagnosis starts with a visit to your doctor to see if your symptoms are being caused by BPH. To determine a BPH diagnosis, your doctor may run a series of tests:
- Physical examination of your prostate
- Review of your symptoms
- Evaluations of your ability to store urine in your bladder and your ability to urinate
If these tests confirm a BPH diagnosis, your doctor will then discuss your treatment options.
References:
- Roehrborm CG, et al. Clin Interv Aging. 2008.
- Data on file, PROCEPT BioRobotics.
- GBD 2019 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Collaborators. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022.
- Foster HE, et al. J Urol. 2018.